The SVOM space mission (SVOM stands for Space based multi-band astronomical Variable Objects Monitor) is a French-Chinese mission dedicated to the detection and study of gamma-ray bursts, and in a larger extent to the transient sky. SVOM has been launched succesfully the 22nd june 2024 from Xichang in China.
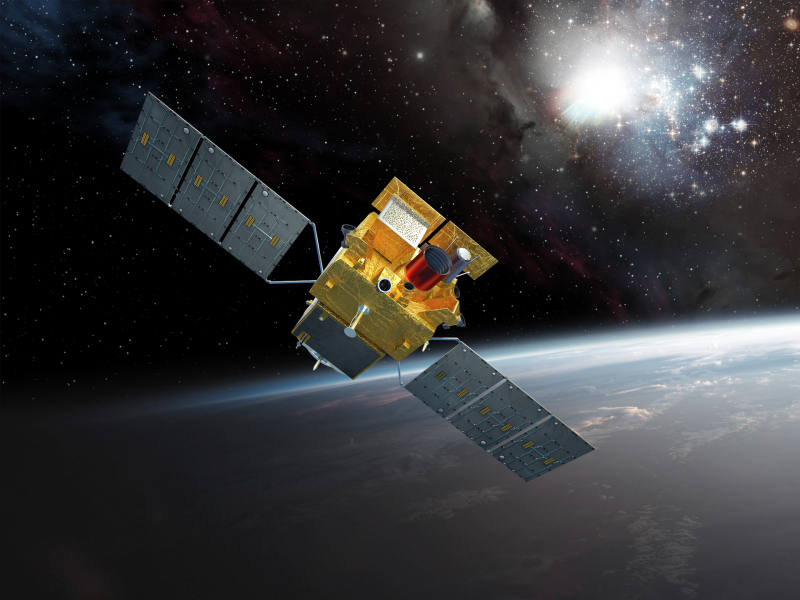

Fig.1. Artistic view of the SVOM satellite. (Crédits CNES)
The gamma-ray bursts (GRB) are intense gamma-ray emission coming from the collapse of massive star or the merging of neutron stars. They are perfect tools to explore the highly-redshifted universe and study the physics in extreme conditions. Moreover they have been recently associated to the emission of gravitational waves an thus play an important role in multi-messenger astrophysics. In addition to the GRB, SVOM will study different transient sources like AGNs, Blazars, etc... in the framework of the General Program (GP).
The transient nature of the phenomena and the rapid fading of the source, makes it difficult to observe. The SVOM mission will consist in several instruments covering a large wavelength coverage to study these phenomenon in more details.
ECLAIRs telescope plays a very important role in the mission since it detects the GRB and provides the first localisation. ECLAIRs is a coded mask telescope covering the x-ray domain (4keV-150keV). Once roughly localised, the satellite slews autonomously and uses its narrow field of view instruments MXT (x-ray) and VT(visible) to provide a better localisation and study the afterglow emission of the GRB. At the same time, an alert is sent to the ground and is collected thanks to a dedicated VHF antenna network and this alert allows our robotic telescopes on the ground to follow the event as well.
APC is in charge of the scientific and mechanical conception of the ECLAIRs coded mask, is in charge of the development of the main scientific pipeline of the ECLAIRs instrument to provide all the scientific products one can extract from the data. In addition, APC is in charge of the organisation of the GP (General Program) and ToO (Target of Opportunity) programs.


APC is also involved in the development of the ECLAIRs scientific pipeline (ECPI). The data analysis consists in several and successive steps that allows to go from the raw data as recorded by ECLAIRs (cf. Fig. 4) to scientific products (cf. Fig. 5) like sky images, lightcurves, spectrum or catalog of sources. The ECLAIRs pipeline runs on the ground in the French Science Center (FSC) infrastructure. The FSC is in charge of the coordination of the different activities of the pipelines of all the intruments and manage the interfaces between the different services (database, API REST...) of the SVOM ground segment.
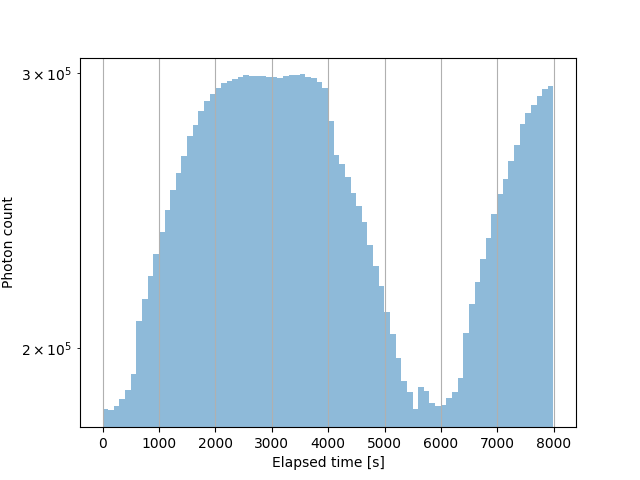
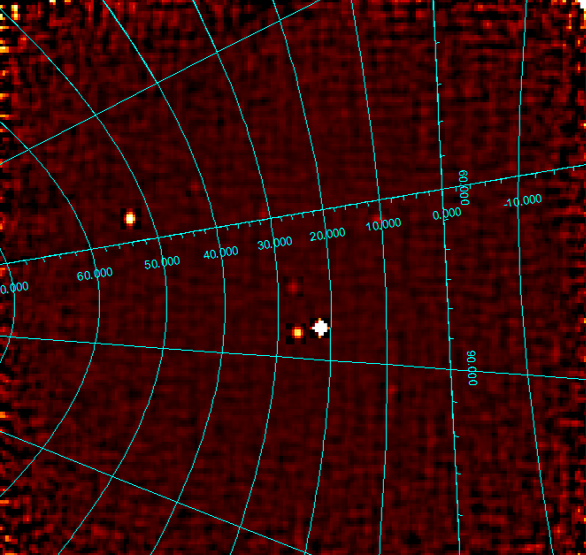
The SVOM mission is a cooperation between the Chinese Space Agency (CNSA) and the French Space Agency (CNES). The duration of the mission is for 5 years with possibility of extensions...
Movie on the SVOM mission
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jwLmvoaXHhc&ab_channel=CNES
SVOM APC Team
Scientists
- LACHAUD Cyril (responsable)
- GOLDWURM Andrea
- COLEIRO Alexis
- CANGEMI Floriane
- FOISSEAU Antoine
Technical and administration
ECLAIRs coded mask team
- GIVAUDAN Alain (Chef de Projet)
- KARAKAC Maurice
- BERTOLI Walter
- DHEILLY Stéphane
- JUFFROY Corinne
Pipeline project team
- CAVET Cécile (Chef de projet)
- BACON Philippe
- JIMENEZ-PEREZ Hugo
- BELLEMONT Nicolas
- DODU Fabrice
- LE STUM Sébastien
Administrative service
- PAVILI-BALADINE Lydie
Links
APC activity report (> 200Mo): 2017-2021
Collaboration website: http://www.svom.fr/svom.html
