Taranis is a CNES microsatellite for the study of transient atmospheric phenomena related to storm activity: Terrestrial Gamma-ray Flashes (TGF), sprites, blue jets, red giants, elves And relations between them. For this purpose, it is equipped with several experiments in visible imaging, electric and magnetic field measurement, electron detection and X and gamma photon measurement. The payload is under the scientific and technical responsibility of LPC2E (Orléans). The preliminary mission review was successfully completed in June 2009. TARANIS is expected to be placed in 2019 in a sun-synchronous orbit at 600-700 km altitude.
APC's expertise in gamma spectrometry led us to design and develop the XGRE (X, Gamma and Relativistic Electrons) instrument dedicated to the detection and measurement of TGF and BTE ("Terrestrial Electrons Beams"), the electron flux generated during the passage of gamma photons from TGFs into the atmosphere.
The TGFs
These events were discovered by NASA's BATSE satellite, dedicated to the study of cosmic gamma ray bursts (see SVOM / ECLAIRS) and confirmed by NASA's RHESSI satellite dedicated to high-energy sun observation. These gamma flashes are about a thousand times shorter than cosmic gamma ray bursts.
They are believed to be the electron braking radiation produced by an avalanche phenomenon over stormy regions at 10 to 20 km altitude. It is possible that the avalanche is triggered by a large atmospheric wave (see AUGER and HESS). The radiation-absorbing atmosphere, especially since its energy is low, the position of the low energy cut in the gamma spectrum provides information on the altitude of the emitting region.
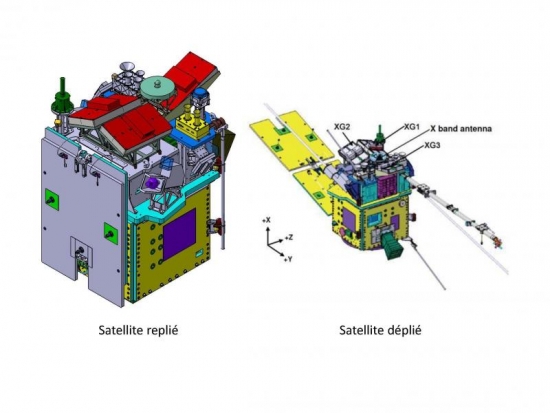
TARANIS Satellite
XGRE
The XGRE instrument on board TARANIS, with a total area of 900 cm2, must distinguish electrons and photons and measure their energy deposits in the 20 keV - 10 MeV range. It must date each TGF and BER with an accuracy of the order of one microsecond and may trigger the other instruments. In addition, it must roughly (30 °) locate the emitting zone and measure as precisely as possible the position of the low energy spectral cut indicating the thickness of the atmosphere passed through. The instrument has 3 sensors, sandwiches composed of 2 plastic scintillators enclosing a lanthanum bromide scintillator (LaBr3). Plastic scintillators are well suited to detecting electrons and LaBr3 is a new scintillator, good gamma spectrometer and very fast. Counting these 3 detectors will deduce the direction of propagation of the particles. The 3 sensors of 300 cm2 each are planar and have angles between them of the order of 40 °. From their relative counts, the direction of the emissive zone will be deduced.
Technical Developments
The TARANIS project includes up to 7 instruments, including the XGRE sensor measuring gamma particles and relativistic electrons from very high altitude flashes.
The XGRE instrument is composed of a sensor and an analyzer card (under CNES), the APC having responsibility for the sensor.
The development of these three sensors required the expertise of the project team in all the following areas:
|
|
|
|
|
|
List of APC staff involved
- ARMANI Johannes Mecanical Fabrication
- BARONICK Jean-Pierre Mecanical Engineering
- BREELLE Eric Instrumentation
- CHAN Kuo Kwan Analog Electronics
- COLONGES Stéphane Produit Electronic Product Insurance
- FRAISSE Eric Financial management
- GRANDSIRE Laurent AIT/AIV (2011-2014)
- JUFFROY Corinne Project and Project Quality
- LAURENT Philippe Scientific Responsible
- LEBRUN François Scientific Responsible (2009-2016)
- LINDSEY-CLARK Miles AIT/AIV/Project Manager
- MEDJDOUB Ghania Quality Assurance Project (NEXEYA)
- NOURY Alexis Digital Electronics FPGA Spatial (2014-2015)
- OLIVETTO Christian Project Manager/Analog Electronics (2009-2015)
- PAILOT Damien Instrumentation
- PETITEAU Manon Quality Assurance Project (NEXEYA) (2010-2014)
- PREVOT Guillaume Instrumentation (2009-2012)
- ROBERT Jean-Luc Communication
- CITERNE Ingrid Gestion Financière (2009-2014)
- LACHACINSKI Benoit Electronique Numérique (2009-2010)
- VERCRUYSSEN Benoit Digital Electronics (2011-2013)
- OUVRAY Xavier Quality Assurance Project (NEXEYA) (2010-2014)
- RICHER Florence Mecanical Engineering (2009-2011)
- KOVACS Alexis Mecanical Engineering (2012-2013)
- MENIVAL Audrey Instrumentation (2010-2011)
- CHAPRON Claude Mecanical Engineering (2010)
Links and Videos
- TARANIS au dessus des orages
- Pourquoi étudier les orages ?
- Vidéo Satellite TARANIS
- Vidéo Instrument XGRE @APC