



Next: Description of the instrument
Up: Description of the instrument
Previous: Contents
A coherent fully polarised radiation
field is represented by a 2 dimensional complex vector field:

which depends
on 3 physical parameters, plus one irrelevant phase. In general a
radiation field is an incoherent superposition of waves with different
polarisations, it is then more convenient to describe the radiation field
statistically through its hermitian ``coherence'' matrix
 :
:
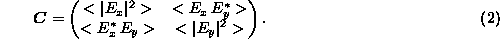
Because of
the mean value that enter its definition, the coherence matrix depends on
4 independent physical parameters, which reduce to 3 for a fully polarised
radiation. These four physical parameters can be chosen to be the
Stokes parameters:
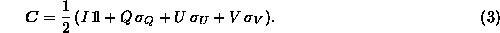
where
matrices 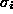 are the usual Pauli matrices :
are the usual Pauli matrices :
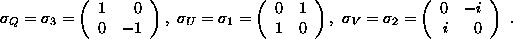
The reason why
we choose to index them in this way should be obvious from relations (3) and
(4).
The Stokes parameters:
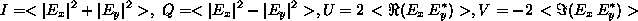
can be deduced from the coherence matrix as:
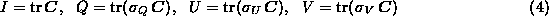
and satisfy the inequality:

which expresses the fact that the polarised energy cannot exceed the
total energy. It becomes an equality
for a fully polarised radiation, thus reducing the number of physical
parameters to 3, as expected.
Jean Kaplan
Wed Sep 19 13:04:59 CEST 2001